Surf EPS: Understanding Epoxy Surfboards and Their Performance
In the world of surfing, the quest for the perfect board is a never-ending journey. Among the myriad of options, surf EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) boards have carved out a significant niche, offering a unique blend of performance characteristics. This article delves into the intricacies of surf EPS technology, exploring its advantages, disadvantages, and how it compares to traditional polyurethane (PU) boards.
Choosing the right surfboard is crucial for optimizing your surfing experience. Factors like wave type, skill level, and personal preference all play a role in the decision-making process. Understanding the materials and construction techniques used in surfboard manufacturing is equally important. That’s where surf EPS comes in. Let’s explore what makes these boards a popular choice among surfers of all levels.
What is EPS Foam?
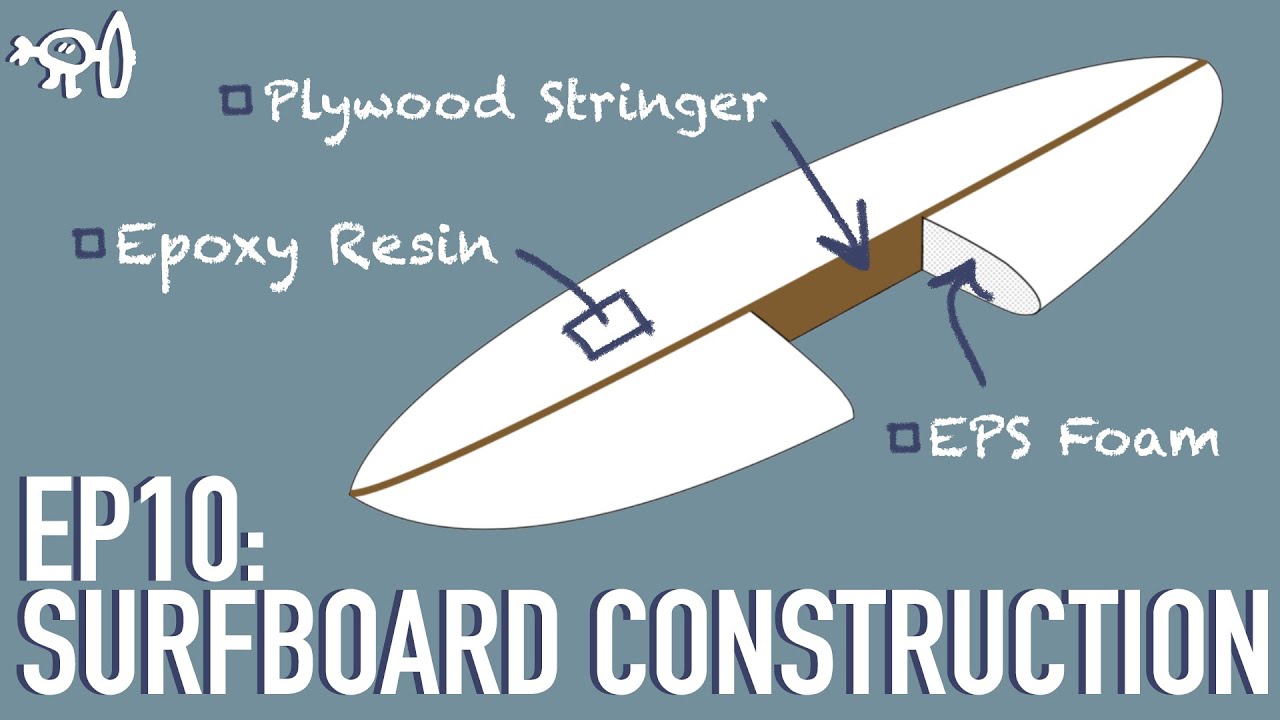
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a closed-cell foam known for its lightweight and buoyant properties. In surfboard construction, EPS foam is used as the core material, providing the board with its shape and floatation. Unlike traditional PU foam, EPS doesn’t absorb water easily, making it more durable and less susceptible to waterlogging. This is a significant advantage for surfers who frequently encounter dings and damage to their boards.
EPS vs. PU Surfboards: Key Differences
The debate between surf EPS and PU surfboards is a long-standing one. Both materials have their pros and cons, and the best choice ultimately depends on individual surfing style and preferences. Here’s a breakdown of the key differences:
- Weight: EPS boards are generally lighter than PU boards, making them easier to paddle and maneuver. This is particularly beneficial for smaller surfers or those surfing in weaker waves.
- Buoyancy: The higher buoyancy of EPS foam allows for increased floatation, making it easier to catch waves and maintain speed.
- Flex: PU boards tend to have a more natural flex pattern, which some surfers prefer for its responsiveness and feel. EPS boards, on the other hand, can feel stiffer, although advancements in construction techniques are constantly improving their flex characteristics.
- Durability: EPS foam is more resistant to water absorption than PU foam, making EPS boards more durable and less prone to waterlogging.
- Cost: Surf EPS boards can sometimes be more expensive than PU boards due to the specialized materials and construction processes involved.
The Construction of a Surf EPS Board
The construction of a surf EPS board typically involves several key steps:
- Core Shaping: The EPS foam core is shaped to the desired dimensions and rocker profile using specialized tools and techniques.
- Glassing: The shaped core is then glassed with epoxy resin and fiberglass cloth. Epoxy resin is used because it bonds better with EPS foam than traditional polyester resin.
- Sanding and Finishing: The glassed board is sanded smooth and finished with a clear coat to protect the epoxy resin and enhance its appearance.
- Fin Installation: Fin boxes are installed to allow for the attachment of fins, which are crucial for controlling the board’s direction and stability.
Advantages of Surf EPS Boards
Surf EPS boards offer several advantages that make them an appealing choice for many surfers:
- Lightweight: The lightweight nature of EPS foam makes these boards easier to paddle, carry, and maneuver, especially for smaller surfers.
- High Buoyancy: The increased buoyancy of EPS foam allows for easier wave catching and improved floatation, making it ideal for beginners and those surfing in weaker waves.
- Durability: EPS foam’s resistance to water absorption makes these boards more durable and less prone to waterlogging, extending their lifespan.
- Performance in Small Waves: The combination of lightweight and high buoyancy makes surf EPS boards excel in small to medium-sized waves, allowing surfers to generate speed and maintain momentum.
- Environmentally Friendly: While not entirely sustainable, EPS foam production can be more environmentally friendly than PU foam production, as it uses less toxic chemicals.
Disadvantages of Surf EPS Boards
Despite their advantages, surf EPS boards also have some drawbacks to consider:
- Stiffness: EPS boards can sometimes feel stiffer than PU boards, which can affect their responsiveness and feel in the water. However, advancements in construction techniques are constantly improving the flex characteristics of EPS boards.
- Delamination: If not properly constructed, surf EPS boards can be prone to delamination, where the epoxy resin separates from the foam core.
- Cost: EPS boards can sometimes be more expensive than PU boards due to the specialized materials and construction processes involved.
- Repair Complexity: Repairing surf EPS boards requires specialized epoxy resin and techniques, which can be more challenging and expensive than repairing PU boards.
Who Should Ride a Surf EPS Board?
Surf EPS boards are a great option for a wide range of surfers, including:
- Beginners: The increased buoyancy and ease of paddling make them ideal for learning to surf.
- Smaller Surfers: The lightweight nature of EPS boards makes them easier to handle and maneuver.
- Surfers in Weak Waves: The high buoyancy allows for better performance in small and mushy conditions.
- Surfers Seeking Durability: The resistance to water absorption makes them a durable option for those who frequently encounter dings and damage.
Tips for Choosing a Surf EPS Board
When selecting a surf EPS board, consider the following factors:
- Wave Type: Choose a board that is suitable for the type of waves you typically surf.
- Skill Level: Select a board that matches your current surfing ability.
- Construction Quality: Look for a board that is well-constructed with high-quality materials.
- Flex Characteristics: Consider the flex pattern of the board and how it will affect its performance.
- Price: Set a budget and compare prices from different manufacturers.
Maintaining Your Surf EPS Board
To prolong the life of your surf EPS board, follow these maintenance tips:
- Rinse with Fresh Water: After each surf session, rinse your board with fresh water to remove salt and sand.
- Store in a Cool, Dry Place: Avoid storing your board in direct sunlight or extreme temperatures.
- Repair Dings Promptly: Repair any dings or cracks as soon as possible to prevent water from entering the foam core.
- Use a Board Bag: Protect your board during transport with a padded board bag.
Advanced EPS Construction Techniques
Beyond the basic construction, advancements are constantly being made to improve the performance and durability of surf EPS boards. These include:
- Carbon Fiber Reinforcements: Adding carbon fiber to the lamination process increases strength and responsiveness.
- Vacuum Bagging: This technique removes excess resin, resulting in a lighter and stronger board.
- Stringerless Designs: Stringerless EPS boards are designed to flex more naturally, providing a more lively feel.
The Future of Surf EPS Technology
Surf EPS technology continues to evolve, with manufacturers constantly innovating to improve performance, durability, and sustainability. As materials and construction techniques advance, surf EPS boards are becoming an increasingly popular choice for surfers of all levels. [See also: Surfboard Materials Comparison] The ongoing research and development in this field promise even more exciting advancements in the future, solidifying the position of surf EPS as a key player in the surfboard market.
In conclusion, surf EPS boards offer a unique combination of lightweight, buoyancy, and durability, making them a versatile option for a wide range of surfers. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of EPS construction, you can make an informed decision and choose the right board to enhance your surfing experience. The evolution of surf EPS continues to shape the future of surfboard design and performance.