EPS Surfboards: Understanding the Performance and Durability of Expanded Polystyrene
In the dynamic world of surfing, innovation is constant. From board shapes to fin designs, surfers and shapers are always pushing the boundaries of performance. One key area of innovation lies in the materials used to construct surfboards. Among the various options available, EPS surfboards, or surfboards made with Expanded Polystyrene foam, have gained significant popularity. This article delves into the specifics of EPS surfboards, exploring their construction, performance characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks to provide a comprehensive understanding for surfers of all levels.
What is EPS Foam?
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a closed-cell foam known for its lightweight and buoyant properties. It’s created by expanding polystyrene beads using steam. This process results in a material composed primarily of air, which contributes to its exceptional floatation. Unlike traditional polyurethane (PU) foam, EPS doesn’t absorb water, making it a more durable option, especially when the outer layers are damaged.
Construction of EPS Surfboards
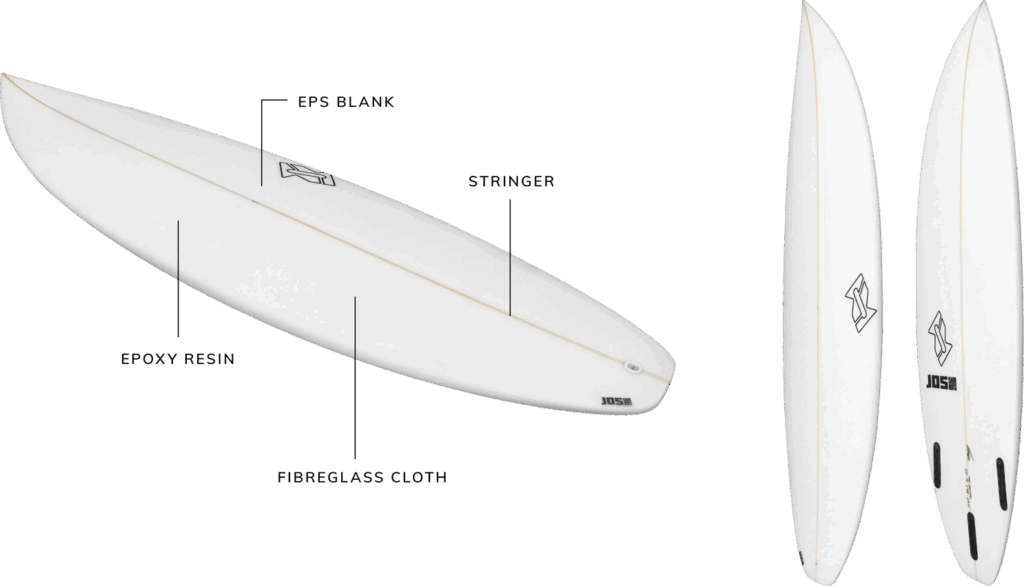
The construction of an EPS surfboard differs slightly from that of a traditional PU board. Here’s a breakdown of the typical process:
- Core Shaping: The process begins with shaping the EPS foam core. Shapers use specialized tools to create the desired board outline, rocker, and foil.
- Glassing: Once the core is shaped, it’s glassed with layers of fiberglass cloth and resin. Epoxy resin is typically used with EPS foam because it bonds better and is more flexible than polyester resin, which is used with PU foam. This flexibility is crucial for maintaining the board’s integrity.
- Fin Installation: Fin boxes are installed to allow for fin attachment. The placement and type of fins significantly impact the board’s performance.
- Sanding and Finishing: The final step involves sanding and polishing the board to achieve a smooth, glossy finish.
Performance Characteristics of EPS Surfboards
EPS surfboards offer a unique set of performance characteristics that appeal to different surfing styles and wave conditions.
Buoyancy and Paddling
The high buoyancy of EPS foam makes these boards exceptionally easy to paddle. This is a significant advantage for surfers of all skill levels, especially in weaker waves or when paddling out through challenging conditions. The increased floatation helps surfers get into waves earlier and with less effort. This is particularly beneficial for longboards or wider boards, which become easier to manage in the water.
Responsiveness and Speed
EPS surfboards are known for their responsiveness and lively feel. The foam’s inherent stiffness allows for efficient energy transfer, resulting in quick acceleration and sharp turns. This responsiveness makes EPS boards ideal for performance surfing and executing radical maneuvers. The board feels more direct and connected to the wave, allowing the surfer to react quickly to changing conditions.
Flex and Drive
The flex characteristics of an EPS surfboard are influenced by the density of the foam and the type of glassing used. Generally, EPS boards tend to have a stiffer flex pattern compared to PU boards. This stiffness can translate to increased drive and projection out of turns, allowing surfers to generate more speed and power. However, some surfers may find the stiffer flex less forgiving in choppy conditions.
Benefits of EPS Surfboards
Choosing an EPS surfboard comes with several advantages:
- Lightweight: EPS surfboards are significantly lighter than traditional PU boards, making them easier to carry and maneuver in the water.
- Buoyancy: The high buoyancy of EPS foam enhances paddling speed and wave-catching ability.
- Durability: EPS foam doesn’t absorb water, making these boards more resistant to water damage and delamination.
- Responsiveness: EPS boards offer a lively and responsive feel, ideal for performance surfing.
- Eco-Friendliness: While not biodegradable, EPS production can be less environmentally harmful than PU production, as it doesn’t involve as many toxic chemicals.
Drawbacks of EPS Surfboards
Despite their advantages, EPS surfboards also have some drawbacks:
- Cost: EPS boards tend to be more expensive than traditional PU boards due to the cost of materials and the more complex construction process.
- Dings: While EPS doesn’t absorb water, it can be more prone to pressure dings than PU foam. The lower density of the foam makes it more susceptible to compression.
- Stiffness: The stiffer flex of EPS boards may not be suitable for all surfers or wave conditions. Some surfers prefer the more forgiving flex of PU boards, especially in choppy or unpredictable waves.
- Repair Complexity: Repairing EPS surfboards requires specific materials and techniques. Using the wrong resin can damage the foam.
EPS vs. PU Surfboards: A Comparison
The choice between EPS and PU surfboards often comes down to personal preference and the type of surfing you plan to do. Here’s a brief comparison:
| Feature | EPS Surfboards | PU Surfboards |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Buoyancy | Higher | Lower |
| Flex | Stiffer | More Flexible |
| Responsiveness | More Responsive | Less Responsive |
| Durability | More Water Resistant | Less Water Resistant |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
PU boards are often favored in powerful, hollow waves where control and drive are paramount. [See also: Best Surfboards for Pipeline] The added weight and flex can help the board hold its line in challenging conditions.
Who Should Ride an EPS Surfboard?
EPS surfboards are a great choice for:
- Beginner Surfers: The increased buoyancy makes paddling and catching waves easier.
- Surfers in Weak Waves: The responsiveness and floatation help generate speed in less powerful conditions.
- Performance Surfers: The lively feel and quick acceleration allow for radical maneuvers.
- Surfers Looking for a Durable Board: The water resistance of EPS foam extends the board’s lifespan.
Tips for Caring for Your EPS Surfboard
To maximize the lifespan of your EPS surfboard, follow these tips:
- Protect from Heat: Avoid leaving your board in direct sunlight or hot cars, as this can cause delamination.
- Use a Board Bag: A board bag provides protection from dings and UV damage.
- Inspect Regularly: Check for any cracks or dings and repair them promptly to prevent water damage.
- Use the Right Repair Kit: Use epoxy resin for repairs to ensure a proper bond with the EPS foam.
The Future of EPS Surfboards
As surfboard technology continues to evolve, EPS surfboards are likely to play an increasingly prominent role. Innovations in foam density, glassing techniques, and board design are constantly improving the performance and durability of EPS boards. Furthermore, as environmental concerns grow, the potential for more sustainable EPS production methods may make these boards an even more attractive option. [See also: Sustainable Surfboard Materials]
Conclusion
EPS surfboards offer a compelling combination of performance, durability, and buoyancy. While they may not be the perfect choice for every surfer or wave condition, their unique characteristics make them a valuable addition to any quiver. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of EPS surfboards, surfers can make informed decisions and choose the right board to enhance their surfing experience. Whether you’re a beginner looking for an easy-paddling board or a seasoned pro seeking a responsive ride, an EPS surfboard might just be the perfect tool for your next session.

