Asymmetric Surfboards: A Comprehensive Guide to Performance and Design
The world of surfing is constantly evolving, with innovations popping up regularly. Among the more intriguing developments in surfboard design is the asymmetric surfboard. These boards, characterized by their different rail shapes on each side, are designed to optimize performance based on the specific demands of heel-side and toe-side turns. This comprehensive guide will delve into the history, design principles, benefits, and considerations of asymmetric surfboards, providing a detailed understanding for surfers of all levels.
The History and Evolution of Asymmetric Surfboards
The concept of asymmetry in surfboard design isn’t new. Early experiments date back to the 1960s and 70s, with pioneers exploring different fin configurations and rail shapes. However, the modern resurgence of asymmetric surfboards can be largely attributed to shapers like Carl Ekstrom and Tom Morey, who refined the designs and brought them to a wider audience. Ekstrom, in particular, developed a sophisticated understanding of how different rail shapes could enhance turning performance, leading to the creation of highly specialized asymmetric surfboards.
Initially, these boards were met with skepticism. Surfers were accustomed to the symmetry of traditional boards, and the idea of riding something different felt unconventional. However, as more surfers experimented with asymmetric surfboards and experienced their unique advantages, their popularity gradually increased. Today, asymmetric surfboards are recognized as a legitimate and effective option for surfers seeking to improve their performance in specific wave conditions.
Understanding the Design Principles
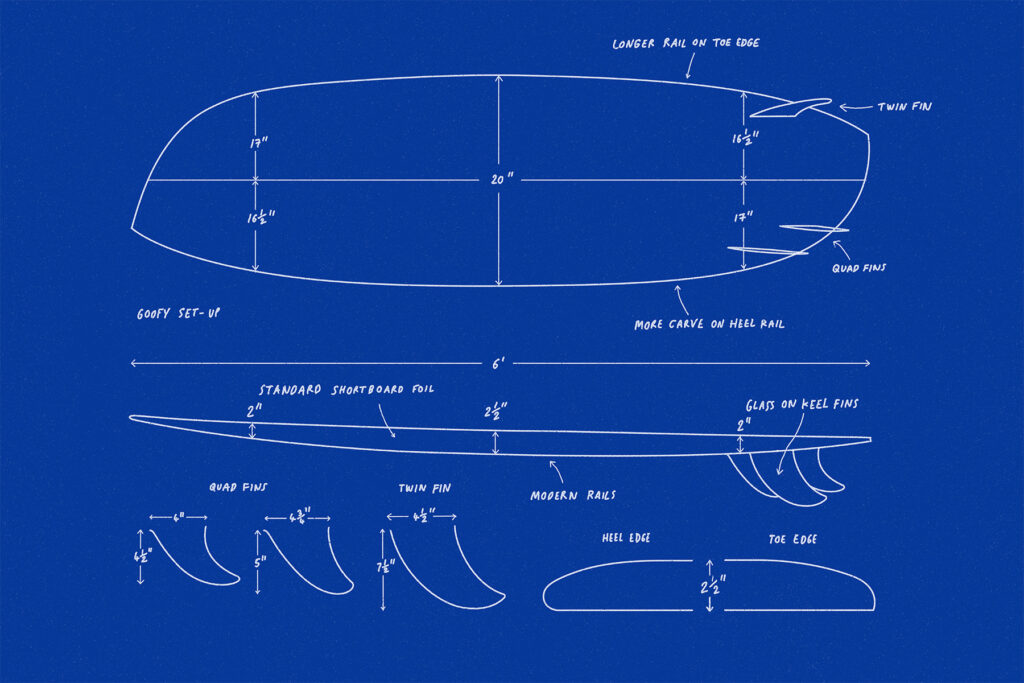
The core principle behind asymmetric surfboards is that heel-side and toe-side turns require different mechanics and leverage points. Heel-side turns typically involve a more drawn-out arc, requiring a longer, more forgiving rail. Toe-side turns, on the other hand, often involve tighter, more abrupt movements, benefiting from a shorter, more responsive rail. By tailoring the rail shape to these specific needs, asymmetric surfboards can provide a more efficient and controlled surfing experience.
Here’s a breakdown of the key design elements:
- Heel-Side Rail: Generally longer and rounder, designed for smooth, drawn-out turns. This rail provides stability and allows for controlled carving.
- Toe-Side Rail: Typically shorter and more angular, designed for quick, responsive turns. This rail offers increased grip and allows for tighter maneuvers.
- Fin Configuration: Fin placement is crucial for balancing the asymmetry. Often, the fins are positioned to complement the rail shapes, further enhancing the board’s turning characteristics. Some asymmetric surfboards feature unique fin setups, such as a quad fin on one side and a single fin on the other.
- Bottom Contour: The bottom contour can also be asymmetrical, with different concaves and channels on each side to further optimize water flow and performance.
Benefits of Riding an Asymmetric Surfboard
The primary benefit of an asymmetric surfboard is improved turning performance. By optimizing the rail shapes for heel-side and toe-side turns, these boards can offer a more responsive and controlled surfing experience. This can lead to:
- Increased Speed and Flow: The tailored rail shapes allow for more efficient water flow, resulting in increased speed and smoother transitions between turns.
- Enhanced Control: The different rail shapes provide greater control and stability, particularly in challenging wave conditions.
- Tighter Turns: The shorter, more angular toe-side rail allows for quicker and more precise turns, enabling surfers to maneuver in tight spaces.
- Improved Performance in Specific Wave Conditions: Asymmetric surfboards can be particularly effective in waves that favor one type of turn over the other. For example, a board designed for predominantly right-hand waves might have a more aggressive toe-side rail to maximize performance on those turns.
Considerations Before Switching to an Asymmetric Surfboard
While asymmetric surfboards offer numerous benefits, they’re not for everyone. Here are some important considerations before making the switch:
- Learning Curve: Getting used to the asymmetrical feel of the board can take some time. It’s important to be patient and willing to experiment with different riding techniques.
- Wave Conditions: Asymmetric surfboards are often designed for specific wave conditions. Choosing the right board for the type of waves you typically surf is crucial.
- Rider Skill Level: While beginners can certainly experiment with asymmetric surfboards, they may be more beneficial for intermediate to advanced surfers who have a solid understanding of turning mechanics.
- Cost: Asymmetric surfboards can be more expensive than traditional boards due to the more complex design and construction process.
Choosing the Right Asymmetric Surfboard
Selecting the right asymmetric surfboard involves considering several factors, including your skill level, the type of waves you typically surf, and your personal preferences. Here are some tips to guide your decision:
- Consult with a Shaper: The best way to find the perfect asymmetric surfboard is to work with an experienced shaper who can tailor the design to your specific needs.
- Consider the Wave Conditions: Think about the type of waves you typically surf. Are they predominantly right-hand or left-hand? Are they steep and powerful or mellow and rolling? The answers to these questions will help you determine the ideal rail shapes and fin configuration.
- Experiment with Different Designs: If possible, try out different asymmetric surfboards before making a purchase. This will allow you to get a feel for the different rail shapes and fin setups and determine which ones work best for you.
- Read Reviews: Research different asymmetric surfboard models and read reviews from other surfers. This can provide valuable insights into the performance and durability of the boards.
The Future of Asymmetric Surfboard Design
The evolution of asymmetric surfboards is ongoing. As shapers continue to experiment with new designs and materials, we can expect to see even more innovative and high-performance boards in the future. One area of focus is the integration of advanced technologies, such as 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD), to create more precise and customized asymmetric surfboards. Another trend is the development of asymmetric surfboards specifically designed for different surfing disciplines, such as longboarding and stand-up paddleboarding.
The asymmetric surfboard represents a significant step forward in surfboard design, offering surfers a unique opportunity to optimize their performance and enhance their surfing experience. While they may not be for everyone, they offer a compelling alternative for those seeking to push their limits and explore new possibilities in the water. The key is to understand the design principles, consider the specific wave conditions, and work with a knowledgeable shaper to find the perfect asymmetric surfboard for your individual needs.
Ultimately, the asymmetric surfboard is a testament to the ongoing innovation and creativity within the surfing community. It’s a reminder that there’s always room for improvement and that by challenging conventional wisdom, we can unlock new levels of performance and enjoyment in the sport we love. Whether you’re a seasoned pro or a beginner just starting out, the world of asymmetric surfboards offers a fascinating glimpse into the future of surfing.
[See also: Surfboard Design Innovations]
[See also: Choosing the Right Surfboard]
[See also: Surfboard Fins Explained]

